Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
What is fMRI?
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or fMRI in short is a type of magnetic resonance imaging (imaging) done to measure neural activity in the brain or spinal cord.
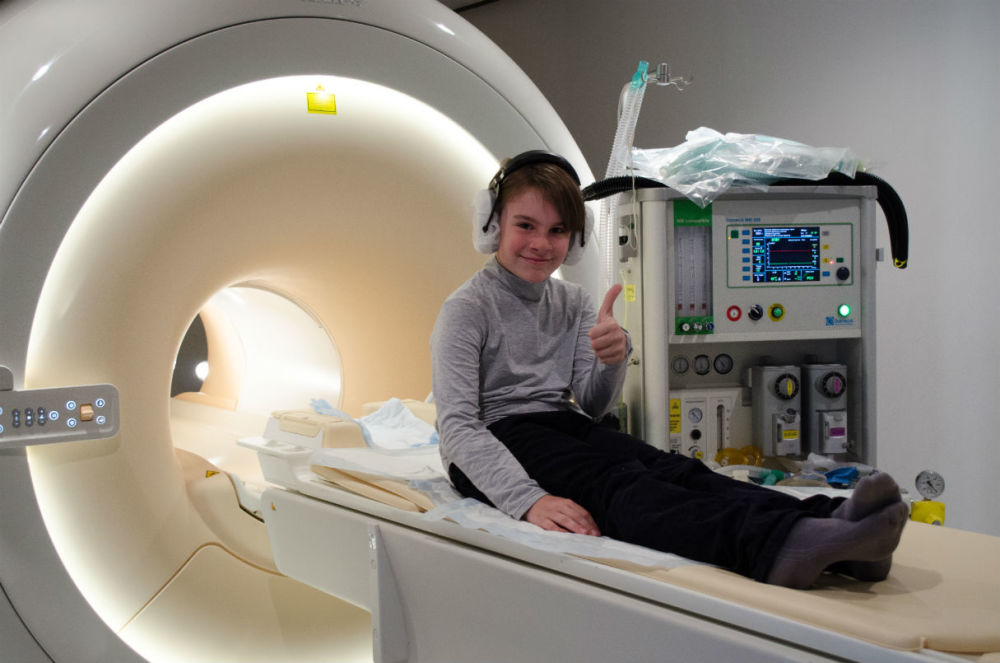
How it works?
The method is based on the fact that cerebral blood flow and the activity of brain neurons are interconnected. When an area of the brain is active, blood flow to this area is increased. The relative concentrations of oxygen-rich and poor blood also change. in the area of activation. These changes are recorded by the scanner as a result of which images of brain activity are obtained; .
How the research is going?
Since MRI is inherently a large magnet, metal in any form cannot be brought into the scanner. In order not to accidentally forget to lay out metal things, the laboratory has a special hand-held metal detector (like the security services have). After checking, our specialists will help you get settled in the scanner. The scanner room can be chilly, so there is a blanket in the scanner for test subjects. During its operation, the scanner makes loud sounds, so it will take some time to get used to them. Ear plugs and special noise-canceling headphones will help to significantly reduce the noise level. Within a few minutes you will not pay attention to its periodic buzzing and crackling. Once you're comfortable in the scanner, we'll start taking brain scans. You are doing the same task as before, inside the scanner, while we are taking images of your working brain. After the research, we will give you brain scans that you can show to your friends (or add to your family album).
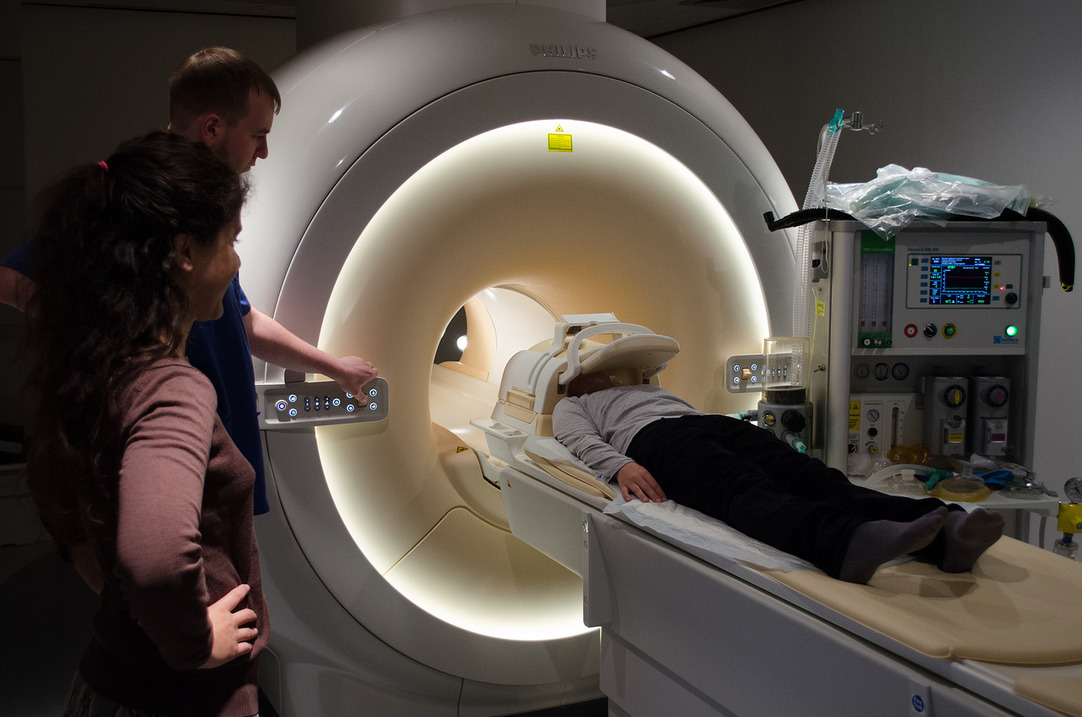
Why it is needed?
fMRI is one of the few ways to look into a working brain without any external influence. Using the method, you can very accurately (up to millimeters) determine which brain structures worked during your task, as well as how these structures “communicated” with each other, transmitting information. This knowledge helps to understand how higher mental functions, such as memory, attention, thinking, are formed from the coordinated work of parts of the brain. Having received pictures of different people, you can establish the individual characteristics of a person, according to which you can later try to predict abilities and predispositions.
Is it safe?
The procedure is absolutely safe if there are no metal objects in the body (pins, plates, pacemakers, etc.). There is no radiation in the tomograph, the scanner is a large magnet, and the magnetic field is completely harmless to humans and animals.
Have you spotted a typo?
Highlight it, click Ctrl+Enter and send us a message. Thank you for your help!
To be used only for spelling or punctuation mistakes.